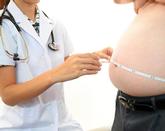
Physical activity boosts brain function in overweight individuals

Exercise has the ability to improve brain function in previously sedentary, overweight individuals.
The University of Tübingen in Germany studied a group of overweight or obese (an average BMI of 31) people, who underwent two brain scans before and after an eight-week exercise intervention, which included cycling and walking.
Previous studies have shown that obese and overweight individuals are prone to insulin resistance in the brain, where it provides information about current nutritional status, as well as the rest of the body.
Led by Dr. Stephanie Kullmann, researchers at Tübingen wanted to know whether exercise can improve insulin sensitivity in the brain and improve cognition in overweight individuals.
Brain function was measured before and after using an insulin nasal spray to investigate insulin sensitivity of the brain. Participants were also assessed for cognition, mood, and peripheral metabolism.
Even though the exercise intervention only resulted in a marginal weight loss, brain functions important for metabolism "normalised" after eight weeks.
Exercise increased regional blood flow in areas of the brain important for motor control and reward processes, both of which depend on the neurotransmitter dopamine.
Dopamine is an important neurotransmitter for learning new motor skills and in reward-related learning and this research shows that exercise significantly improves dopamine-related brain function.
One area in particular, the striatum, had enhanced sensitivity to insulin after the eight weeks of exercise such that the brain response of a person with obesity after exercise training resembled the response of a person with normal-weight. Interestingly, the greater the improvement in brain function, the more belly fat a person lost during the course of the exercise intervention.
Behaviourally, participants reported an improvement in mood and task switching, which is an indicator for improved executive function.
"The bottom line is that exercise improves brain function," said Kullmann.
"And increasing insulin sensitivity in dopamine-related brain regions through exercise may help decrease the risk of a person to develop type 2 diabetes, along with the benefits for mood and cognition."
The study was presented during the annual meeting of the Society for the Study of Ingestive Behavior. For more informational, click here.

Centre Manager
Director of Operations
Fitness Motivator
Recreation Assistant/Lifeguard (NPLQ required)
Membership Manager
Recreation Assistant
Duty Manager (Dry)
Swim Teacher
Swim Teacher
Chief Executive Officer, Mount Batten Centre
Swim Teacher
Swimming Teacher
Swimming Teacher
Company profile

Featured Supplier

Property & Tenders
Company: Knight Frank
Company: Belvoir Castle
Company: AVISON YOUNG
Company: London Borough of Bexley
Company: Forestry England